News
IGiG Summer Internships 2025
26-03-2025
 The Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformatics presents a proposal of paid summer internships for students for 2024. The internships duration is up to three months. The titles and topics of the internships are in the appendix. The deadline for submitting applications is May 16, 2025. Please contact the tutors of individual internships directly (e-mail).
The Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformatics presents a proposal of paid summer internships for students for 2024. The internships duration is up to three months. The titles and topics of the internships are in the appendix. The deadline for submitting applications is May 16, 2025. Please contact the tutors of individual internships directly (e-mail). more...
more...IGiG scientific seminar - Prof. Christian Heipke
06-03-2025
 IGiG is pleased to invite to a scientific seminar, which will take place on March 13, 2024 (Thursday) at 9:00 AM in the Room 100G (institute library), Grunwaldzka Street 53, Wrocław (Building C1). Prof. Christian Heipke from Leibniz University Hannover will give a lecture: "AI in photogrammetry and remote sensing".
IGiG is pleased to invite to a scientific seminar, which will take place on March 13, 2024 (Thursday) at 9:00 AM in the Room 100G (institute library), Grunwaldzka Street 53, Wrocław (Building C1). Prof. Christian Heipke from Leibniz University Hannover will give a lecture: "AI in photogrammetry and remote sensing".Abstract: Photogrammetry is a technique for image capture and analysis, as well as 3D reconstruction from images, which has its roots in the 19th century. When space images became available, remote sensing was added to the name of the discipline. Recently, also the term computer vision has been extensively used to describe essentially the same methods, techniques and algorithms.
 more...
more...IGiG scientific seminar - Prof. Thomas P. Kersten
26-02-2025
 IGiG is pleased to invite to a scientific seminar, which will take place on March 6, 2024 (Thursday) at 9:00 AM in the Room 100G (institute library), Grunwaldzka Street 53, Wrocław (Building C1). Prof. Thomas P. Kersten from HafenCity University Hamburg will give a talk on "Historical 3D City Models as an Immersive Experience in Virtual Reality”.
IGiG is pleased to invite to a scientific seminar, which will take place on March 6, 2024 (Thursday) at 9:00 AM in the Room 100G (institute library), Grunwaldzka Street 53, Wrocław (Building C1). Prof. Thomas P. Kersten from HafenCity University Hamburg will give a talk on "Historical 3D City Models as an Immersive Experience in Virtual Reality”.Abstract: Virtual reality is becoming an affordable and interesting tool for visualisations in a variety of fields, including architecture, planning and monument preservation. This is due to the increasing power of 3D documentation and modelling technologies. Consequently, there is a growing need to develop efficient methods for the detailed creation of immersive virtual 3D environments. This technology is therefore becoming an attractive form of knowledge transfer for institutions such as museums and other cultural educational institutions, which often work within a tight budget.
 more...
more...Schedule of IGiG seminars in the summer semester 2024/2025
22-01-2025
 The Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformatics warmly invites you to attend a series of scientific seminars during the summer semester. Continuing our tradition, the meetings will take place in the IGiG library (room 100G) on Thursdays from 9:00 to 10:00 AM (unless otherwise noted). The seminars will feature presentations by experienced researchers from leading institutions as well as emerging young scientists.
The Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformatics warmly invites you to attend a series of scientific seminars during the summer semester. Continuing our tradition, the meetings will take place in the IGiG library (room 100G) on Thursdays from 9:00 to 10:00 AM (unless otherwise noted). The seminars will feature presentations by experienced researchers from leading institutions as well as emerging young scientists.- 18.02.2025 r. - Dr. Guergana Guerova, Sofia University, "GNSS Storm Nowcasting Demonstrator".
- 20.02.2025 r. - Dr hab. inż. Dariusz Gotlib, Politechnika Warszawska, "Perspektywy rozwoju i wyzwania współczesnej kartografii".
- 06.03.2025 r. - Prof. Dr.-Ing. Thomas P. Kersten, HafenCity Universität Hamburg, "Historical 3D City Models as an Immersive Experience in Virtual Reality".
- 13.03.2025 r. - Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Christian Heipke, Leibniz Universität Hannover,
"AI in photogrammetry and remote sensing".
- 17.04.2025 r. - Dr. Saeid Haji-Aghajany, Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy we Wrocławiu, "Shaping the Future: AI Applications in Tropospheric Analysis".
 more...
more...
IGiG scientific seminar - Dr. Guergana Guerova
17-01-2025
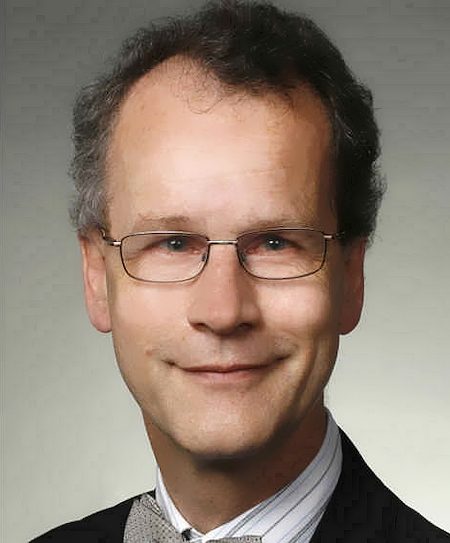
 IGiG is pleased to invite to a scientific seminar, which will take place on February 18, 2025 (Tuesday) at 9:00 AM in the Room 100G (institute library), Grunwaldzka Street 53, Wrocław (Building C1). Dr. Guergana Guerova from the University of Sofia will present a lecture "GNSS Storm Nowcasting Demonstrator".
IGiG is pleased to invite to a scientific seminar, which will take place on February 18, 2025 (Tuesday) at 9:00 AM in the Room 100G (institute library), Grunwaldzka Street 53, Wrocław (Building C1). Dr. Guergana Guerova from the University of Sofia will present a lecture "GNSS Storm Nowcasting Demonstrator".Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is an established atmospheric monitoring technique delivering water vapour data in near-real time with a latency of 90 min for operational Numerical Weather Prediction in Europe within the GNSS water vapour service (E-GVAP). The advancement of GNSS processing made the quality of real-time GNSS tropospheric products comparable to near-real-time solutions. In addition, they can be provided with a temporal resolution of 5 min and latency of 10 min, suitable for severe weather nowcasting.
 more...
more...Archive: « PREVIOUS PAGE | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | NEXT PAGE »
 |
 |
 |
 |
Contact
|
INSTITUTE OF GEODESY AND GEOINFORMATICS
Wroclaw University of Environmental and Life Sciences Grunwaldzka 53 50-357 Wroclaw NIP: 896-000-53-54, REGON: 00000 18 67 Phone +48 71 3205617 Fax +48 71 3205617 e-mail: igig@upwr.edu.pl |